
"Everyone is a genius. But if you judge a fish on its ability to climb a tree, it will live its whole life believing that it is stupid."
-Albert Einstein

Welcome to Ms. Stephens Environmental Science Class
Email: [email protected]
Class website: www.astephensscience.com
Tutorial: 3:45-4:45 Wednesdays, or schedule an appointment.
Announcements:
The class website contains lesson plans, notes, and study links. Please check the lesson plans to see what you missed, and for make-up work.
Notice to Parents & Students:
The class website is regularly updated for each unit. Students are expected to check the class website prior to the next class when they are absent to not get behind. There are many study resources available as well!
** Please download the Course Syllabus by clicking the link above and confirm you have read the course syllabus by completing the google form in your google class room. Codes for the classrooms are in the syllabus.
Mission Possible at Maynard Jackson High School
Prezi of Class procedures and rules
Class Procedures Quiz
Give me 5 Standards of EVS
Project: About me/One small thing
Video: Before the Flood
Video thinking guide
Online Multiple Intelligence Test - Save As. to save the graph of your results, print, email me, or save using copy ScreenShot and paste in a word doc. Bring results to class.


Unit 1: Human Impact: Cause and Effect
(August 1-Oct. 6)
SEV4. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information to analyze human impact on natural resources.
a.Construct and revise a claim based on evidence on the effects of human activities on natural resources.
b. Design, evaluate, and refine solutions to reduce human impact on the environment including, but not limited to, smog, ozone depletion, urbanization, and ocean acidification.
Essential Questions:
1. How does pollution affect land, air, and water?
2. How does air pollution affect water resources?
Intro to Land Resources: (August 1-12, 2022)
SWBAT obtain, evaluate, and communicate information to analyze human impact on natural resources IOT construct and revise a claim based on evidence on the effects of agriculture, forestry, ranching, mining, urbanization, and pollution on land and organisms.
(Lesson 1.1)
Unit 1 Vocabulary List
Text References:
Chapter 1 Section 1 pgs. 14–15
Chapter 1 ppt
Chapter 1 guided notes
Engage:Georgia Land Use interactive map
Questions:
1.What are the key patterns in land use change in Georgia?
2.What are the causes and effects of these patterns?
Lab Activity:
Complete a mining lab using cookies.
Link: http://www.earthsciweek.org/classroom-activities/cookie-mining
This lab demonstrates for students the considerations that must take place when using land as a natural resource.
Cookie Sheet:
Mining for Chocolate activity
http://www.earthsciweek.org/classroom-activities/cookie-sheet
Homework:
Evaluate: Choose one of the following writing prompt to summarize the importance of land and organism conservation.
Prompt 1: It is estimated that we are losing 137 plant, animal and insect species every day due to the deforestation of rainforests. That means we are losing over 50,000 species every year. The reasonthe land is being cleared is for the timber, for mining operations and to provide grazing areas for large scale cattle ranching. What do you think can or should be done to stop the deforestation?
Prompt 2:
A tract of land is being sold in your community. Fictitious bidders include the National Park Service, a children’s hospital, a shopping-mall developer, an oil drilling company, and the U.S.Armed Forces. Choose one and become a lobbyist for one that group writing arguments on behalf of their interests.
Introduction to Water Resources: (August 14-25)
SWBAT obtain, evaluate, and communicate information to analyze human impact on natural resources IOT construct and revise a claim based on evidence on the effects of fishing, water use, desalination, and waste water treatment on water and organisms. (Lesson 1.2)
Lesson 1.2 (Water)
Classroom Activity:
Overfishing Link to Activity: https://serc.carleton.edu/eslabs/fisheries/4.html
Link to Article: https://www.nefsc.noaa.gov/history/stories/groundfish/grndfsh1.html#a rt
Hands-On Lab:
Water Quality testing in the classroom
Virtual Lab option:
Students will engage in a virtual lab to test water and document their findings for each sample.
Link: http://www.glencoe.com/sites/common_assets/science/virtual_labs/CT04/CT04.html
Guiding Questions:
1.What other issues can water have besides too much lead?
2.How does the treatment process address issues with the water quality?
Homework:
Use the following writing prompt to summarize the importance of water and organism conservation.
Prompts:
Water is life. There is the same amount of water now on Earth as when it was first created. For us,it’s easy.
we turn on the tap and there it is. Yet in Africa and Asia, women and children spend about 6 hours a day and walk an average of 3.7 miles a day just to collect water, according to water.org. This is time they could be spending in school or caring for their families. Think of five
ways you and your family could conserve water so that everyone can do their part.
Introduction to Air Resources:(August 28-Sept 8)
SWBAT obtain, evaluate, and communicate information to analyz e human impact on natural resources IOT construct and revise a claim based on evidence on the effects of agriculture, forestry, ranching, mining, urbanization, and pollution on air and organisms. (Lesson 1.3)
Video: China's toxic smog
Guiding Questions:
1.What did you observe?
2.What are some of the effects of air pollution in North China?
3.Why do you think that China is so polluted?
Activity: The State of Air
Link: http://www.stateoftheair.org/
Investigation Handout: State of the Air.pdf
Begin to reason and understand that there are multiple issues factors that cause air quality issues. This activity will help you understand that there are multiple factors and that some of the factors have a greater impact than others.
Guiding Questions:
1.What is ground level ozone and what effects does it have?
2.What are particulates and are all particulates harmful?
Human Impact: (Sept. 11-22)
SEV4. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information to analyze human impact on natural resources.
b. Design, evaluate, and refine solutions to reduce human impac t on the environment including, but not limited to, smog, ozone depletion, urbanizati on, and ocean acidification
SWBAT design, evaluate, and refine solutions IOT to reduce human impact on the environment including, but not limited to, smog, ozone depletion, urbanization, and ocean acidification. ( Lesson 2.1)
Essential Questions:
1. What information did you use from prior lessons to decide which problem you consider the most important to reduce?
2.Which resource (land, water, air) is most effected by smog, ozone depletion, urbanization,and acidification?
Chapter 2 Section 3 pgs. 38–42
Video: What do Environmental Engineers do?
Guided questions:
1.How would you describe the job of an environmental engineer?
Performance Assessment: Design and Engineer a process that solves a problem related to human impact on land, air, water, and organisms.
Project Resource:
Water Filtration Project
Claim-Evidence-Reasoning (CER)
Claim: Statement that answers the question.
Evidence: Information that supports the claim. Scientific data comes from observations in natural settings or controlled experiments, measurements, or valid scientific sources. Personal information comes from opinions, beliefs, and everyday experiences.
Reasoning: The justification that links the evidence to the claim. It explains why the evidence supports the claim. Scientific reasoning includes a scientific principle.
Human Impact: Food and Agriculture (Sept. 25-Oct.6)
SEV4. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information to analyze human impact on natural resources.
c.Construct an argument to evaluate how human population growth affects food demand and food supply (GMOs, monocultures, desertification, Green Revolution).
SWBAT obtain, evaluate, and communicate information to analyze human impact on natural resources IOT construct an argument to evaluate how human population growth affects food demand and food supply. (Lesson 3.1)
Essential Questions: What affect does scarcity of food have on food quality?
Unit 1 Summative Assessment: October 12/13
Unit 2: Ecology (total time 7 weeks)
Chapter 4: The Organization of Life
Environmental Science: Holt pages 98-113
Notes:
Videos:
Biotic and abiotic factors

Secondary Text: We will be reading this text in class.
Zoo by James Patterson
Zoo BINGO Book Club Choice Board
Zoo BINGO Book Club Reference Link

2B: Ecology:
Standards: SEV3 d,e, SEV5 c.
SWBAT: differentiate between the three types of symbiotic relationships IOT contruct an explaination that predicts patterns of interactions among organisms across multiple ecosystems.(SEV3.e)
SWBAT: demonstrate how they personally impact the ecosystem they inhabit IOT calculate their ecological footprint.(SEV5.c)
SWBAT: demonstrate how human kind has permanently changed the earth in both negative and positive ways IOT develop a feasible plan to conserve the earth.(SEV5.c)
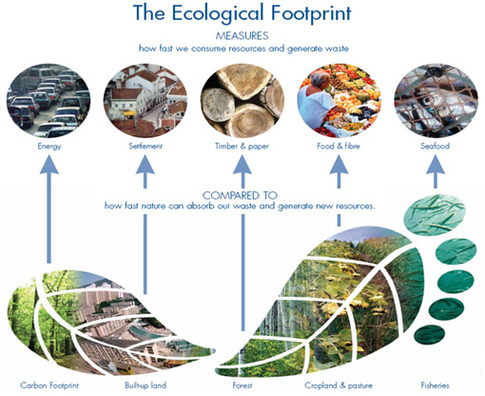
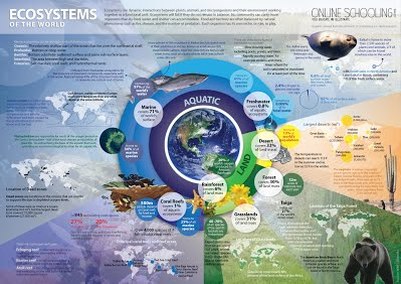
Chapter 6: Biomes

Chapter 7: Aquatic Ecosystems
Environmental Science: Holt pages 184-207
Aquatic Biome Project


Unit 3
Populations
Chapter 8: Understanding Populations
Environmental Science: Holt
pages 210-223
Below you find the classroom assignments and PPT's used for Chapter 8, Understanding Populations. You may use this website for access to PPT's, guided notes, and make up assignments.
Chapter 9: The Human Population
Environmental Science: Holt
pages 234-247
Below you find the classroom assignments and PPT's used for Chapter 9, The Human Population. You may use this website for access to PPT's, guided notes, and make up assignments.
Unit 4
Populations
Chapter 10: Biodiversity
Environmental Science: Holt
pages 258-275
Below you find the classroom assignments and PPT's used for Chapter 10, Biodiversity. You may use this website for access to PPT's, guided notes, and make up assignments.